
Metal Tubes for Automotive Engines
Metal tubular components for oil, coolant and pneumatic circuits in automotive engines
Motorbacs has more than 16 years of development and manufacturing experience in engine metal tube assemblies, with an annual production capacity exceeding 10 million units. With deep technical expertise and engineering accumulation, we work closely with customers from the early design stage, participating in layout planning and cost optimization, and providing feasible design solutions that meet installation space constraints and performance requirements.
Samples
Production Process
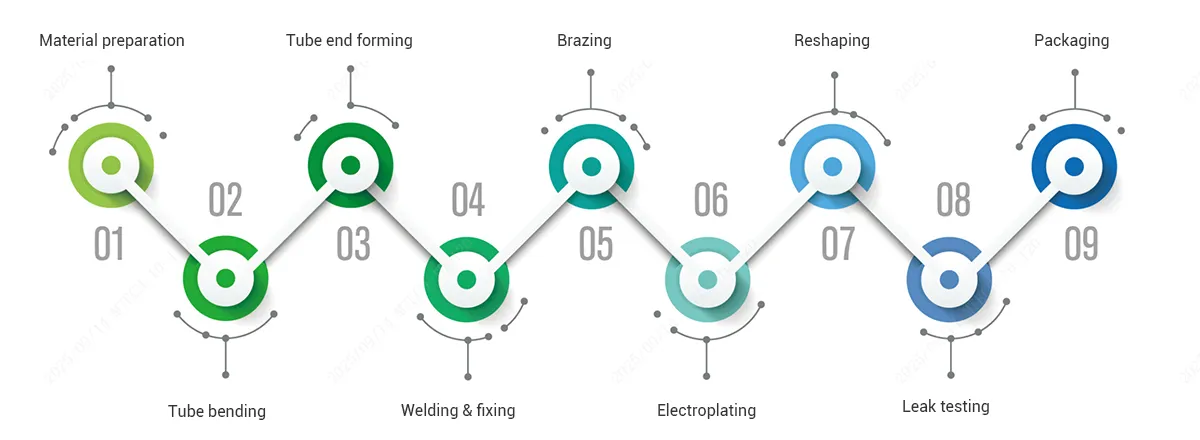
- Material preparation
- Tube bending
- Tube end forming
- Welding & fixing
- Brazing
- Electroplating
- Reshaping
- Leak testing
- Packaging
Features
| Product Type | Material | Welding Method | Welding Strength | Airtightness | Neutral Salt Spray Test |
| Engine Coolant Tubes | Stainless steel | Brazing | ≥ 350 N/mm² or greater than base material strength | 0.5–0.8 MPa no leakage, or leakage rate < 0.2 ml/min under 0.5 MPa pressure | Chromate coating – 500 hours no red rust |
| Carbon steel + Surface treatment | Brazing | ≥ 350 N/mm² or greater than base material strength | 0.5–0.8 MPa no leakage, or leakage rate < 0.2 ml/min under 0.5 MPa pressure | 1000 hours no red rust | |
| Engine Oil Tubes | Stainless steel | Brazing | ≥ 350 N/mm² or greater than base material strength | 0.5–0.8 MPa no leakage, or leakage rate < 0.2 ml/min under 0.5 MPa pressure | Chromate coating – 500 hours no red rust |
| Carbon steel + Surface treatment | Brazing | ≥ 350 N/mm² or greater than base material strength | 0.5–0.8 MPa no leakage, or leakage rate < 0.2 ml/min under 0.5 MPa pressure | 1000 hours no red rust |
Our Workshops













