Laser Welded High-Strength Steel Tubes
High-strength steel tubing for new-energy automotive chassis and lightweight structural components

Laser-welded tubes are widely used in ≥800 MPa high-strength steel roll-forming and high-speed welding applications:
- Minimal deformation & high precision
Laser welding of high-strength steel produces extremely small weld deformation, ensures high dimensional accuracy, delivers stable welding quality, provides high joint strength, reduces energy consumption, and eliminates the need for post-weld heat treatment. - Lightweight & higher performance for NEV chassis
When applied to new-energy vehicle chassis, laser-welded high-strength steel tubes can achieve 10–30% weight reduction, while improving strength, rigidity, and fatigue performance by 30–50%. - Growing demand with new-energy vehicle development
As the global demand for new-energy vehicles continues to expand, the demand for laser-welded high-strength steel tubes will continue to grow in parallel.
Inspection Requirements
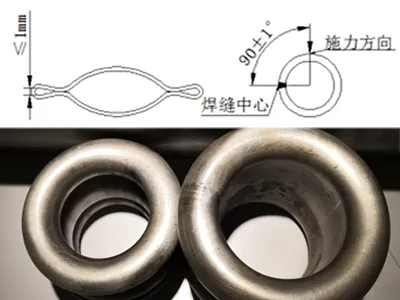
Performance Testing: Flattening / Flaring
- Standard distance between compression plates after flattening < 2T + 1 mm;
- National standard requirement: distance between plates = 1/3 of the pipe outer diameter;
- Under both standards, the welded seam must show no cracks, tears, or weld failure to be qualified.
- For the flaring test, a 200–300 mm section is taken and a 180° flanging test is performed using a special mold.
- Qualification requirement: no tearing or cracking at the weld seam during outward flanging of the pipe wall
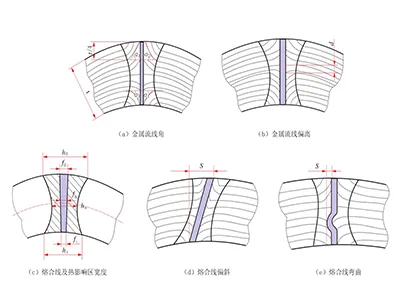
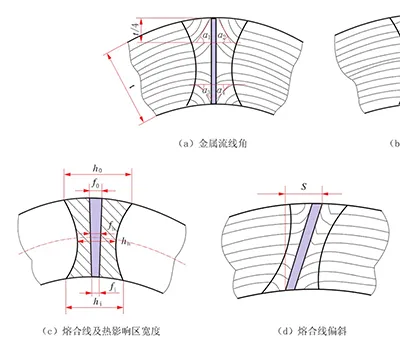
Metallographic Testing: Fusion Line
- Japan Nippon Steel standard width: 0.02–0.20 mm
- Germany standard width: 0.02–0.12 mm
- Korea PSP standard width: 0.05–0.30 mm
- Standard fusion line width of the weld zone is controlled within 0.02–0.11 mm, observed under 100× microscope